Investigating the Homogenization of
Web Design Using Computer Vision
We’re looking for participants for an ongoing study! If you or someone you know has been involved in web design since the mid-2000’s, please find out more here!
HCI is interested in how the everyday interfaces we encounter shape our perception of society. For example, search engines help us more easily navigate the web, but their centralization gives them the ability to perpetuate and normalize harmful societal biases. Developing tools to identify centralized control over our interfaces is an important first step towards understanding the potential harms. In this paper, we investigate the growing concern that visual design of the World Wide Web has homogenized over the past decade by developing automatic techniques to characterize and quantify this possible homogenization. In particular, we apply two types of computer vision techniques, deep learning with convolutional neural networks and hand-engineered color and layout features, each with complementary strengths and weaknesses. Our results show that designs have become more similar since 2007, especially for page layouts, where the average distance between sites decreased by over 30%. We investigate potential causes of this homogenization including overlap in source code and web libraries, color scheme standardization, and support for mobile devices. We hope our results motivate further discussion of the factors which influence designers and the implications of these factors on the future trajectory of the web.
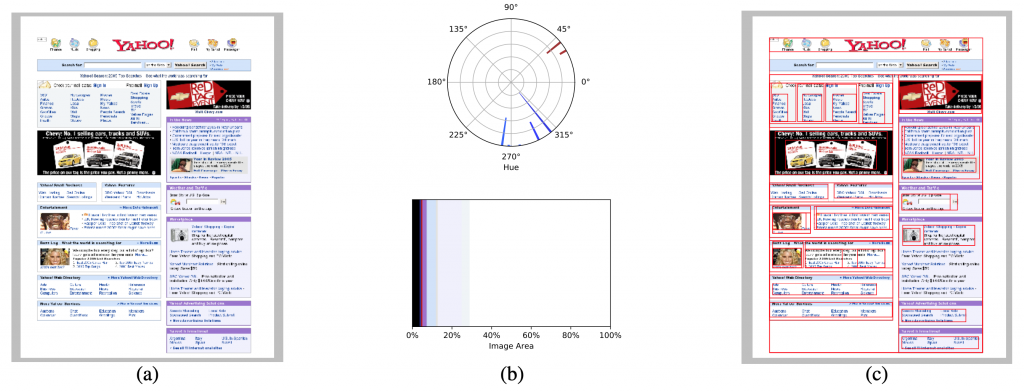
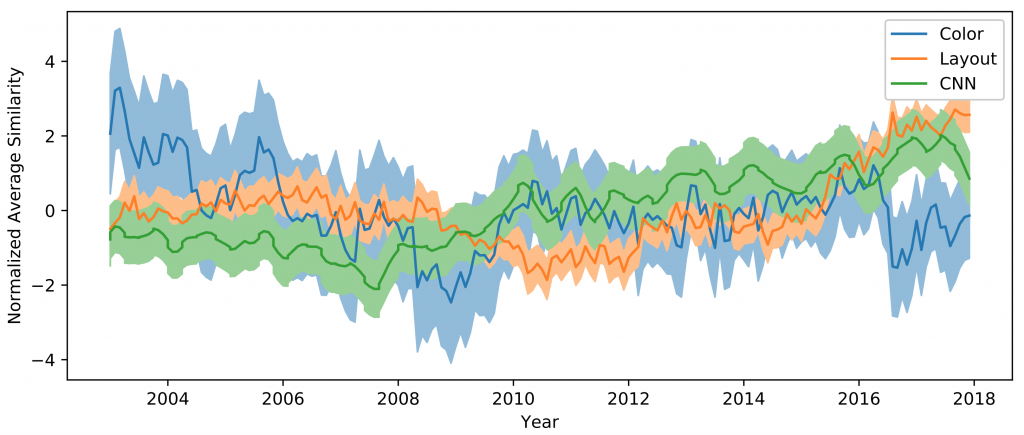
Arguably, the homogenization of design may signal that a few corporations have gained influence over what constitutes proper design on web.
This project is ongoing research! We are preparing our work for publication and plan to update this page with code and data later on.